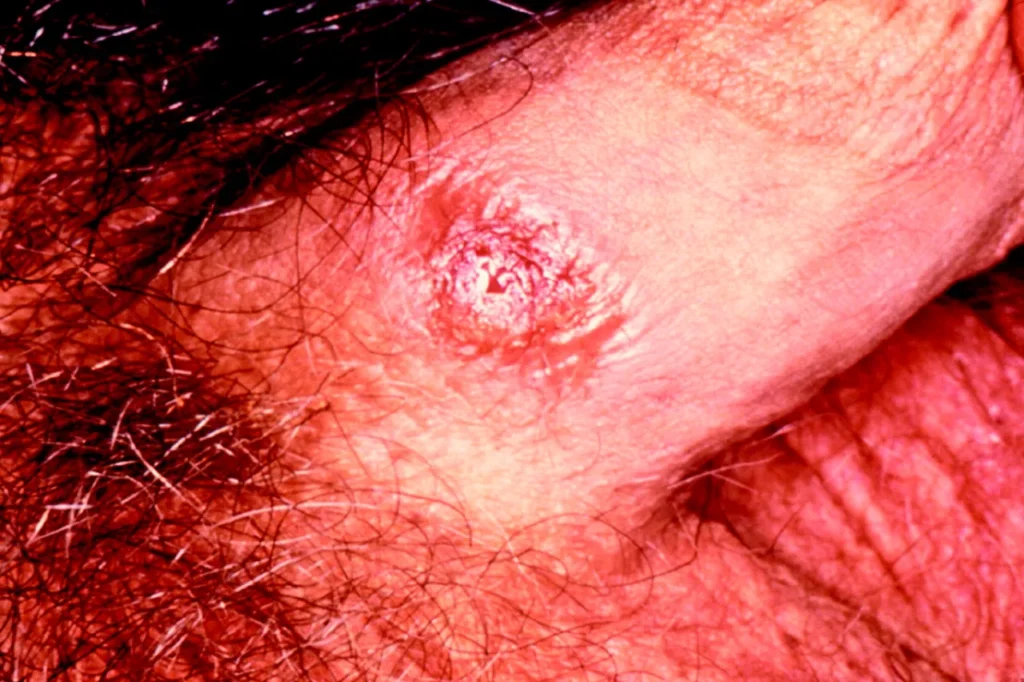
Understanding Long-Term Complications Of Syphilis
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum. While it can be easily treated with antibiotics in the early stages, if left untreated, it can lead to severe long-term complications. Understanding these complications is crucial in order to raise awareness about the importance of early detection and treatment.
One of the most significant long-term complications of syphilis is neurosyphilis. This occurs when the infection spreads to the nervous system, affecting the brain and spinal cord. It can lead to various neurological symptoms, such as headaches, difficulty coordinating movements, and even paralysis. In advanced stages, neurosyphilis can cause dementia, personality changes, and problems with concentration and memory.
Another complication of syphilis is cardiovascular syphilis. This occurs when the infection affects the heart and blood vessels. Over time, the bacteria can cause inflammation and damage to the walls of the blood vessels, leading to conditions such as aortic aneurysm (weakening and bulging of the aorta) and aortic regurgitation (leaking of the aortic valve).
- Furthermore, untreated syphilis can also result in gummas, which are soft, tumor-like growths that can develop in various organs of the body. These gummas usually form in the skin, bones, liver, or other organs, and can cause significant damage if left untreated. In addition to gummas, syphilis can also lead to chronic inflammation of the bones and joints, known as osteitis.
| Long-term Complications | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Neurosyphilis | Headaches, coordination difficulties, dementia |
| Cardiovascular syphilis | Aortic aneurysm, aortic regurgitation |
| Gummas | Tumor-like growths in various organs |
| Osteitis | Chronic inflammation of bones and joints |
It is important to note that these long-term complications of syphilis can occur several years after the initial infection. This emphasizes the significance of regular follow-up and monitoring, even after successful treatment of the primary infection. Periodic blood tests and medical check-ups can help detect and manage any potential complications before they become severe.
understanding the long-term complications of syphilis is crucial in raising awareness about the importance of early detection and treatment. Neurosyphilis, cardiovascular syphilis, gummas, and osteitis are just some of the potential complications that can arise if syphilis is left untreated. Regular follow-up, monitoring, and timely intervention play a vital role in minimizing the impact of these complications and promoting better long-term outcomes for syphilis patients.
The Impact Of Untreated Syphilis On Patients
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection caused by a bacterium called Treponema pallidum. If left untreated, syphilis can have a significant impact on the health and well-being of affected individuals. This blog post explores the consequences and long-term complications that can arise from untreated syphilis.
Untreated syphilis can progress through several stages, each with its own set of symptoms and potential complications. In the primary stage, a painless sore called a chancre appears at the site of infection. If the infection is not treated, it can progress to the secondary stage, characterized by a rash, fever, and flu-like symptoms. Without appropriate medical intervention, the infection can enter the latent stage, where it remains dormant and may not cause any symptoms for an extended period.
However, the consequences of untreated syphilis can be severe. In the late or tertiary stage, syphilis can affect multiple organ systems, including the heart, brain, blood vessels, and bones. The infection can lead to cardiovascular complications such as aortic aneurysms and heart valve abnormalities. Neurosyphilis, a condition in which the bacteria invade the central nervous system, can result in symptoms such as dementia, paralysis, and severe headaches.
- Furthermore, untreated syphilis can have devastating effects on pregnancies. Pregnant individuals with syphilis can pass the infection to their unborn babies, leading to congenital syphilis. This condition can cause stillbirth, premature birth, low birth weight, and a range of physical and developmental abnormalities in infants.
| Stage | Symptoms | Complications |
|---|---|---|
| Primary | Chancre, usually painless | None |
| Secondary | Rash, fever, flu-like symptoms | Lesions on mucous membranes, skin, and other organs |
| Latent | No symptoms | Not applicable |
| Tertiary | Cardiovascular and neurological symptoms | Aortic aneurysms, heart valve abnormalities, dementia, paralysis |
To prevent the long-term impact of untreated syphilis, early diagnosis and effective treatment are crucial. Medical professionals recommend regular screening for sexually active individuals, particularly those with risk factors such as multiple sexual partners, unprotected sex, or a history of sexually transmitted infections. Timely treatment with antibiotics such as penicillin can eradicate the infection and prevent further complications.
untreated syphilis can have a profound impact on patients’ overall health and quality of life. The infection can progress through various stages, leading to severe complications affecting multiple organ systems. Pregnant individuals with syphilis are at risk of transmitting the infection to their babies, causing congenital syphilis. Timely diagnosis, treatment, and regular follow-up are essential in preventing the long-term consequences of untreated syphilis and promoting better health outcomes for affected individuals.
Progression Of Syphilis Symptoms Over Time
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum. It can be transmitted through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex, as well as through close contact with infected skin or mucous membranes. The infection progresses in stages, each characterized by distinct symptoms and complications.
In the primary stage, a firm, painless sore called a chancre develops at the site of infection. This sore usually appears within 3 weeks of exposure and can be easily overlooked or mistaken for a harmless bump or ulcer. Because of this, many people with syphilis do not seek early treatment and unknowingly progress to the secondary stage.
The secondary stage is marked by a variety of symptoms that typically appear 2 to 8 weeks after the development of the chancre. These symptoms may include a rash, usually on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet, as well as flu-like symptoms such as fever, headache, sore throat, and fatigue. Without appropriate treatment, the infection can enter a latent stage where no symptoms are present, but the bacteria remain in the body and can cause serious damage to the internal organs.
- Long-term complications:
- Cardiovascular complications
- Neurological complications
- Visual impairments
- Hearing loss
| Stage | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Primary | Chancre at the site of infection |
| Secondary | Rash, flu-like symptoms |
| Latent | No symptoms present |
Exploring The Potential For Relapses In Syphilis Patients
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum. It is typically spread through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex. If left untreated, syphilis can lead to serious complications and long-term health problems. One such concern is the potential for relapses in syphilis patients.
Relapses occur when there is a recurrence of symptoms after a period of apparent recovery. In the case of syphilis, a relapse can happen even after successful treatment with antibiotics. This is because the bacterium responsible for syphilis can remain dormant in the body for years, and then become active again.
The exact triggers for relapses in syphilis patients are not well understood. However, certain factors may increase the risk. These include a weakened immune system, such as in individuals with HIV/AIDS, as well as the presence of other sexually transmitted infections. individuals who engage in high-risk sexual behaviors or have multiple sexual partners may be more susceptible to relapses.
- It is important for healthcare providers to educate syphilis patients about the potential for relapses and the need to continue monitoring their health even after successful treatment. Regular follow-up appointments and testing are crucial to detect any recurrence of the infection and prevent further complications.
| Factors influencing relapse risk: |
|---|
| 1. Weakened immune system: Individuals with HIV/AIDS or other conditions that compromise the immune system are more prone to relapses. |
| 2. Co-infection with other STIs: The presence of other sexually transmitted infections, such as gonorrhea or chlamydia, can increase the risk of relapse. |
| 3. Risky sexual behaviors: Engaging in unprotected sex or having multiple sexual partners can heighten the chances of relapses. |
Managing relapses in syphilis patients involves prompt detection and appropriate treatment. Healthcare providers may need to adjust the antibiotic regimen based on the severity of the relapse and the individual’s response to previous treatment. In some cases, a longer duration of antibiotic therapy may be necessary to effectively eradicate the infection.
Furthermore, it is crucial for syphilis patients to receive support and counseling to address any emotional or psychological impact of the disease. The potential for relapses can cause anxiety and stress, and having a healthcare professional or support group to turn to can greatly assist in coping with these challenges.
Prevention is also key in reducing the risk of relapses. Practicing safe sex, including consistent and correct use of condoms, can significantly lower the chances of acquiring or transmitting syphilis. Regular testing for syphilis and other sexually transmitted infections is essential, especially for individuals at higher risk.
while successful treatment of syphilis with antibiotics can eliminate the infection, there is always the potential for relapses in patients. Understanding the factors that influence relapse risk and addressing them through regular monitoring, appropriate treatment, and supportive care are vital in preventing complications and promoting the overall well-being of syphilis patients.
Long-Term Prognosis For Syphilis Patients With Early Treatment
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum. If left untreated, it can lead to severe complications and long-term health issues. However, when syphilis is diagnosed early and treated promptly, the prognosis for patients is generally favorable, with minimal long-term complications. Early treatment plays a crucial role in preventing the progression of the disease and reducing the risk of complications.
One of the key advantages of early treatment for syphilis is the prevention of long-term complications that can significantly impact a patient’s health. When syphilis is detected in its primary or secondary stages, treatment with antibiotics such as penicillin can effectively eliminate the infection and prevent the disease from progressing further. Timely intervention not only resolves the immediate symptoms but also reduces the likelihood of more severe complications that may arise in later stages of syphilis.
Achieving a successful long-term prognosis for syphilis patients greatly depends on the early detection and initiation of appropriate treatment. Regular screening and testing for syphilis, especially for individuals at higher risk, are crucial to identify the infection at an early stage. Prompt treatment significantly reduces the risk of transmission to others and improves the chances of a positive outcome for the infected individual.
- Factors influencing long-term outcomes:
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Stage of infection | The stage at which syphilis is diagnosed and treated affects the long-term prognosis. Early stages have a better prognosis compared to late stages. |
| Effective treatment | The choice of appropriate antibiotics and adherence to the prescribed treatment plan significantly impacts the long-term outcome of syphilis infection. |
| Coexisting health conditions | Underlying health conditions or weakened immune systems can influence the progression and severity of syphilis and its long-term prognosis. |
The long-term prognosis for syphilis patients with early treatment is generally favorable, with minimal complications. However, it is important to note that individuals who have had syphilis may still face certain risks and challenges. Regular follow-up and monitoring by healthcare professionals are essential to detect any potential relapses or complications and provide appropriate treatment promptly. With proper management and ongoing care, syphilis patients who receive early treatment can achieve positive long-term outcomes and lead healthy lives.
Managing Late-Stage Complications Of Syphilis
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacteria Treponema pallidum. If left untreated, syphilis can progress to late-stage complications, which can have severe consequences for individuals affected. Late-stage syphilis can affect various parts of the body, including the heart, brain, nerves, bones, and skin. Managing late-stage complications of syphilis requires comprehensive medical care and ongoing monitoring to mitigate potential long-term effects.
One of the primary complications of late-stage syphilis is neurosyphilis, which affects the central nervous system. Neurosyphilis can manifest in various forms, including asymptomatic neurosyphilis, meningovascular neurosyphilis, and general paresis. Asymptomatic neurosyphilis occurs when there are no apparent neurological symptoms, making it challenging to detect and diagnose. Meningovascular neurosyphilis, on the other hand, involves inflammation of the blood vessels in the meninges and can lead to stroke-like symptoms.
In managing late-stage complications of syphilis, a multidisciplinary approach is crucial. A team of healthcare professionals, including infectious disease specialists, neurologists, cardiologists, dermatologists, and psychiatrists, may be involved in the care of patients. Treatment typically involves a combination of antibiotics, such as penicillin, administered intravenously or via intramuscular injection. The specific treatment plan depends on the stage of syphilis and the organs affected. Close monitoring of the patient’s condition may also be necessary to assess the response to treatment and identify any potential relapses.
- Table:
| Complication | Treatment |
|---|---|
| Neurosyphilis | High-dose intravenous or intramuscular penicillin |
| Cardiovascular syphilis | Cardiovascular evaluation and potentially surgery |
| Gummatous syphilis | Penicillin or other appropriate antibiotics |
Patients with late-stage syphilis may also require supportive care to manage symptoms and improve overall quality of life. Depending on the complications experienced, additional treatments such as physical therapy, speech therapy, or occupational therapy may be necessary. Psychological and emotional support is also essential, as individuals with late-stage syphilis may face significant mental health challenges due to the impact of the disease on their lives.
managing late-stage complications of syphilis is a complex process that requires comprehensive medical care, including multidisciplinary collaboration and ongoing monitoring. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent long-term consequences. providing supportive care and addressing the mental health concerns of syphilis survivors contribute to their overall well-being and recovery. By raising awareness, promoting prevention measures, and advocating for regular screening and follow-up, we can work towards a brighter future where the impact of syphilis is minimized.
Factors Influencing Long-Term Outcomes In Syphilis Patients
Blogging about factors influencing long-term outcomes in syphilis patients is crucial in order to shed light on this important aspect of the disease. Throughout this article, we will discuss the various factors that can impact the long-term outcomes of syphilis patients, ranging from individual characteristics to treatment options. By understanding these factors, healthcare providers can develop more effective strategies for managing and treating syphilis, ultimately improving the overall prognosis for patients.
One key factor that influences the long-term outcomes of syphilis patients is the stage at which the disease is diagnosed and treated. Early detection and prompt treatment are essential in preventing the progression of syphilis and minimizing potential complications. Patients who receive immediate treatment during the early stages of syphilis have a higher chance of achieving a favorable long-term outcome. This highlights the importance of regular screening and early intervention as key components of syphilis management.
In addition to the timing of diagnosis and treatment, other factors such as underlying medical conditions and immune response play a significant role in influencing long-term outcomes. Individuals with pre-existing health conditions, such as HIV/AIDS, may experience more severe symptoms and complications as a result of syphilis. Furthermore, the strength of the immune response can affect the body’s ability to fight off the infection. Patients with compromised immune systems may have a higher risk of developing long-term complications.
The Importance Of Regular Follow-Up And Monitoring
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum. Without adequate treatment, it can lead to serious long-term complications. Therefore, regular follow-up and monitoring are crucial aspects of managing syphilis. This blog post will discuss the importance of regular follow-up and monitoring in syphilis patients, highlighting the benefits it offers in terms of early detection, prevention of further complications, and ensuring optimal treatment outcomes.
An essential aspect of regular follow-up and monitoring in syphilis patients is the early detection of any potential complications. Syphilis can progress through different stages, with each stage presenting distinct symptoms. Regular monitoring allows healthcare providers to closely examine and track the progression of the infection, ensuring timely intervention at the earliest signs of complications.
Furthermore, regular follow-up and monitoring play a crucial role in preventing further complications. Syphilis can affect various organs and systems in the body if left untreated or inadequately treated. Through regular check-ups, healthcare providers can assess the effectiveness of the ongoing treatment, identify any limitations or challenges, and make adjustments accordingly to prevent the development of severe complications.
- regular follow-up and monitoring are essential for ensuring optimal treatment outcomes. Syphilis treatment typically involves a course of antibiotics, such as penicillin. However, the duration and type of treatment may vary depending on various factors, such as the stage of the infection, the presence of co-infections, and individual patient characteristics. By closely monitoring the patient’s progress, healthcare providers can assess the response to treatment and make any necessary modifications to ensure complete eradication of the infection.
| Regular Follow-Up and Monitoring in Syphilis |
|---|
| Early detection of complications |
| Prevention of further complications |
| Optimizing treatment outcomes |
Addressing Mental Health Concerns In Syphilis Survivors
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum. While it is a treatable disease, the impact of syphilis extends beyond its physical symptoms. Addressing mental health concerns in syphilis survivors is an essential aspect of their overall well-being and recovery.
One of the primary mental health concerns that syphilis survivors may experience is stigma and shame. Due to the historical context surrounding syphilis as a taboo and often associated with immoral behavior, individuals who have had syphilis may feel stigmatized and experience shame or guilt. This can have a profound effect on their mental health, leading to feelings of anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem.
Another mental health concern in syphilis survivors is the potential for post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Individuals who have gone through the experience of syphilis and its treatment may have endured physical discomfort, side effects of medication, and the fear of transmitting the infection to others. These traumatic experiences can lead to the development of PTSD, manifesting as intrusive thoughts, nightmares, and heightened anxiety.
Supportive Care And Lifestyle Adjustments For Syphilis Patients
The topic of supportive care and lifestyle adjustments for syphilis patients is of utmost importance in ensuring the well-being and recovery of individuals affected by this sexually transmitted infection. While medical treatments play a significant role in managing syphilis, the implementation of supportive care measures and lifestyle adjustments can greatly contribute to the overall healing process and improve the quality of life for patients.
Supportive care encompasses a range of interventions aimed at addressing the physical, emotional, and social needs of syphilis patients. This multidimensional approach involves the provision of adequate medical support, counseling services, and the integration of lifestyle adjustments to promote a holistic recovery journey.
One crucial aspect of supportive care for syphilis patients is the management of physical symptoms and complications. This requires close collaboration between healthcare professionals and patients to monitor the progress of the infection, address potential side effects of treatment, and offer appropriate remedies for any lingering symptoms. Regular check-ups, blood tests, and imaging may be necessary to ensure the effectiveness of treatment and identify any new developments.
- Moreover, emotional support is paramount in helping syphilis patients cope with the psychological impact of the infection. Receiving a diagnosis of syphilis can evoke feelings of shame, guilt, and anxiety, making it essential for healthcare providers to offer empathetic and non-judgmental support. Counseling services can assist patients in processing their emotions, managing stress, and developing proactive coping strategies. By addressing the emotional well-being of patients, supportive care significantly contributes to their mental health and overall recovery process.
| Supportive Care Strategies for Syphilis Patients: |
|---|
| 1. Education and Information: Providing comprehensive education about syphilis, its complications, and treatment options empowers patients to actively participate in their recovery journey. This includes knowledge about safe sexual practices, regular follow-ups, and the benefits of adherence to prescribed medications. |
| 2. Lifestyle Adjustments: Adopting a healthy lifestyle can greatly contribute to the overall well-being of syphilis patients. This entails engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a balanced diet, and avoiding alcohol and tobacco use. Such adjustments not only support the body’s healing process but also enhance the immune system. |
| 3. Community Support: Encouraging the involvement of support groups, online communities, or local organizations can provide syphilis patients with a sense of belonging and understanding. Engaging in discussions with individuals who have shared similar experiences can provide emotional support and valuable insights. |
supportive care and lifestyle adjustments for syphilis patients are vital components of a comprehensive treatment approach. By addressing a patient’s physical, emotional, and social needs, healthcare providers can foster a supportive environment that enhances the recovery process and improves the patient’s quality of life. Through education, lifestyle adjustments, and community support, the journey to recovery becomes a collective effort that promotes awareness, empowerment, and a brighter future for syphilis patients.
Success Stories And Inspiring Recovery Journeys
When it comes to sexually transmitted infections, the focus is often on prevention, treatment, and the potential long-term complications. However, it is equally important to shed light on the success stories and inspiring recovery journeys of individuals who have overcome these challenges and reclaimed their lives. These stories not only inspire hope but also highlight the importance of timely diagnosis, proper treatment, and ongoing support. Here, we will delve into some remarkable success stories of individuals who have triumphed over syphilis and the lessons we can learn from their experiences.
One remarkable success story is that of Sarah, a 32-year-old woman who was diagnosed with late-stage syphilis. Despite experiencing a range of severe symptoms, including neurological complications, Sarah refused to succumb to despair. With the support of her healthcare team and loved ones, she embarked on a comprehensive treatment plan combining antibiotics and various supportive therapies. Over time, Sarah’s condition improved significantly, and she regained her physical and mental wellbeing.
Another inspiring recovery journey is that of John, a 45-year-old man who lived with untreated syphilis for several years. He initially ignored the early signs and symptoms, hoping they would resolve on their own. However, as the disease progressed and began affecting his overall health, John realized the gravity of the situation. With the help of a dedicated team of healthcare professionals, John underwent intensive treatment and made significant lifestyle adjustments to support his recovery. Today, he serves as a vocal advocate, spreading awareness and encouraging others to seek help.
Promoting Awareness And Prevention For A Brighter Future
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection that has been a public health concern for centuries. Although advances in medicine have led to effective treatments, the prevalence of syphilis remains a global issue. To combat this persistent problem, it is crucial to promote awareness and prevention strategies for a brighter future.
One key aspect of promoting awareness is educating the public about the transmission and consequences of syphilis. Many people may be unaware of the dangers associated with this infection, including the potential for long-term complications. By disseminating accurate information through various channels, such as social media campaigns, educational materials, and public health initiatives, we can increase knowledge and understanding of syphilis.
Another vital component of promoting a brighter future is emphasizing the importance of prevention. The primary mode of syphilis transmission is through sexual contact, but it can also be transmitted from mother to child during pregnancy or through blood transfusions. Encouraging safe sexual practices, including the consistent use of condoms, getting tested regularly, and practicing abstinence or mutual monogamy, can significantly reduce the risk of syphilis transmission.
- it is crucial to address the stigma surrounding syphilis and other sexually transmitted infections. Overcoming the fear of judgment or discrimination is essential for individuals to seek testing, treatment, and support. By creating a supportive and non-judgmental environment, we can empower those affected by syphilis to seek the care they need, ultimately contributing to a brighter future.
| Key Points: | – Promoting awareness and prevention is crucial for combating syphilis. |
|---|---|
| – Educating the public about the transmission and consequences of syphilis is necessary to increase awareness. | |
| – Emphasizing prevention strategies, such as safe sexual practices and regular testing, can reduce the risk of transmission. | |
| – Addressing the stigma surrounding syphilis is essential for individuals to seek testing, treatment, and support. |