The Importance Of Diagnosis And Treatment
When it comes to syphilis, early diagnosis and prompt treatment are crucial for effective management of the disease. The importance of diagnosis and treatment cannot be emphasized enough, as syphilis can have serious implications on both the individual’s health and public health.
First and foremost, early diagnosis allows for timely intervention, preventing the disease from progressing to more advanced stages. Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum. It can have various symptoms depending on the stage of infection, making it important for individuals to seek medical attention if they notice any unusual signs or symptoms.
Furthermore, early diagnosis facilitates the implementation of appropriate treatment strategies. Syphilis can be effectively treated with antibiotics, particularly penicillin. However, it is essential to select the right dosage and duration of treatment based on the stage of syphilis and individual factors such as allergies or pregnancy. This highlights the importance of proper diagnosis, as misdiagnosis or delayed treatment can lead to suboptimal outcomes.
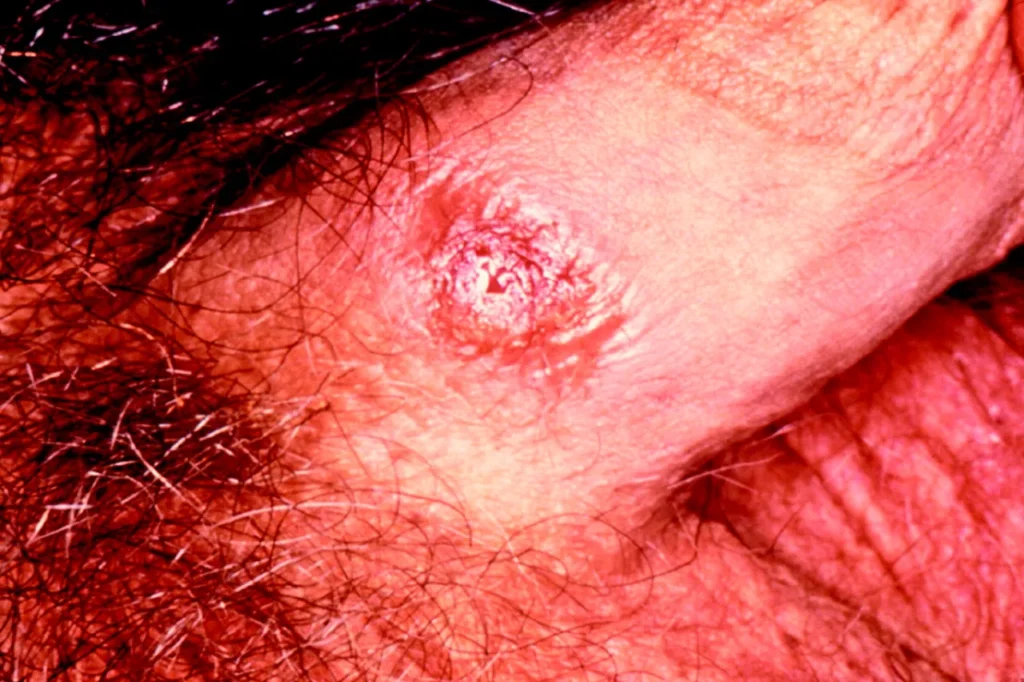
- Primary syphilis: This is the initial stage of syphilis, typically characterized by the development of a painless sore or ulcer called a chancre. The chancre is usually found at the site of infection, such as the genitals, anus, or mouth.
- Secondary syphilis: If left untreated, syphilis can progress to the secondary stage, where a variety of symptoms may occur, including skin rashes, fever, swollen lymph nodes, and sore throat.
- Latent syphilis: This stage is characterized by the absence of visible symptoms. The infection remains in the body but may not be actively causing any noticeable signs or symptoms. However, the bacterium can still be transmitted to others.
- Tertiary syphilis: Without appropriate treatment, syphilis can progress to the late or tertiary stage, which can involve severe complications affecting various organs, such as the heart, brain, and nerves.
the importance of timely diagnosis and treatment of syphilis cannot be overstated. It not only helps prevent the spread of the disease but also ensures that individuals receive the necessary care to manage the infection and prevent complications. If you suspect you may have been exposed to syphilis or are experiencing any symptoms, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
| Potential Side Effects of Syphilis Medications: | Tips for Proper Medication Adherence: | Drug Interactions and Precautions: |
|---|---|---|
| While antibiotics are used to treat syphilis, they can also have potential side effects. It is important to be aware of these side effects and discuss them with your healthcare provider. | To ensure the effectiveness of syphilis treatment, it is crucial to adhere to the prescribed medication regimen. This includes taking the medication as directed, completing the full course of treatment, and avoiding any missed doses. | If you are taking other medications or have any underlying medical conditions, it is essential to inform your healthcare provider. They can assess potential drug interactions and recommend precautions to avoid any adverse effects. |
Different Stages Of Syphilis: What You Need To Know
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum. It is a chronic disease that progresses in different stages if left untreated. The different stages of syphilis include primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary. It is important to understand the characteristics and progression of each stage in order to recognize the symptoms and seek appropriate treatment. Here, we will explore the different stages of syphilis and what you need to know about each.
Primary Syphilis:
In the primary stage of syphilis, a small, painless sore called a chancre appears at the site of infection, usually the genitals, anus, or mouth. This sore typically develops around 3 weeks after exposure to the bacteria. The chancre may go unnoticed or be mistaken for a harmless bump, and it will heal on its own within a few weeks. However, even if the sore disappears, the infection is still present in the body and can progress to the next stage.
Secondary Syphilis:
If left untreated, syphilis will progress to the secondary stage. This stage is characterized by a wide range of symptoms that can affect various parts of the body. Common symptoms include a rash, usually on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet, fever, swollen lymph nodes, sore throat, patchy hair loss, muscle aches, and fatigue. These symptoms may come and go for up to a year or more if syphilis is left untreated. Without proper treatment, the infection can advance to the next stage.
Latent Syphilis:
In the latent stage, syphilis becomes dormant and does not cause any noticeable symptoms. This stage is divided into two sub-stages: early latent syphilis and late latent syphilis. Early latent syphilis refers to the first year after the initial infection, while late latent syphilis refers to the period after the first year. During the latent stage, the infection can still be transmitted to sexual partners, even without symptoms. Without treatment, latent syphilis can progress to the final stage.
Prescription Medications For Primary Syphilis
Primary syphilis is the initial stage of the sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum. It is crucial to promptly diagnose and treat primary syphilis to prevent the infection from progressing to more severe stages. Prescription medications play a crucial role in the treatment of primary syphilis, aiding in the eradication of the bacteria and minimizing the risk of complications.
For the effective treatment of primary syphilis, healthcare professionals commonly prescribe penicillin as the first-line medication. Penicillin is an antibiotic that directly targets the Treponema pallidum bacteria and inhibits its growth. It is typically administered as an intramuscular injection, and the dosage and duration of treatment depend on the stage and severity of the infection. In some cases, individuals who are allergic to penicillin may receive alternative antibiotics such as doxycycline or tetracycline to eliminate the bacteria.
It is essential for individuals undergoing treatment for primary syphilis to strictly adhere to the prescribed medication regimen. Completing the full course of antibiotics is crucial to eradicate the infection completely and prevent relapse or the progression to the next stage of syphilis. Ensure that you follow the instructions provided by your healthcare provider and take the medication as directed.
Choosing The Right Antibiotics For Secondary Syphilis
When it comes to treating syphilis, choosing the right antibiotics is crucial, especially in the case of secondary syphilis. Secondary syphilis occurs in individuals who have not received adequate treatment during the primary stage or have not received any treatment at all. This stage is characterized by a wide range of symptoms, including skin rashes, fever, sore throat, and muscle aches. If left untreated, secondary syphilis can progress to the later stages of the disease, causing severe complications.
In order to effectively combat secondary syphilis, healthcare providers rely on antibiotics to eliminate the infection. The most commonly used antibiotics for treating syphilis are penicillin and its derivatives, including benzathine penicillin G and procaine penicillin G. These antibiotics work by interfering with the growth and reproduction of the bacteria responsible for syphilis, known as Treponema pallidum. It is important to note that individuals who are allergic to penicillin may require alternative antibiotic options, such as doxycycline or tetracycline.
Treating secondary syphilis with the appropriate antibiotics is crucial not only to alleviate symptoms but also to prevent further complications and transmission of the disease. It is essential for healthcare providers to thoroughly evaluate each patient’s medical history, allergies, and overall health condition before prescribing any antibiotics. Compliance with the prescribed antibiotic regimen is also important to ensure the effectiveness of treatment. Regular follow-up visits and testing are necessary to monitor progress and confirm the successful eradication of the infection. By choosing the right antibiotics based on individual considerations, healthcare providers can effectively treat secondary syphilis and help prevent its progression to more severe stages.
Treatment Options For Latent Syphilis
Latent syphilis is a stage of the sexually transmitted infection that occurs when the initial symptoms of syphilis have resolved but the bacteria still remain in the body. This stage is characterized by the absence of external signs or symptoms, making it difficult to diagnose without proper testing. However, despite the lack of visible symptoms, it is important to seek treatment for latent syphilis to prevent the infection from progressing and causing serious complications.
There are several treatment options available for latent syphilis, depending on the duration of the infection and the individual’s medical history. The most common form of treatment is the use of antibiotics, specifically penicillin. Penicillin is considered the most effective treatment for syphilis and is usually administered through injections.
In some cases, individuals may be allergic to penicillin or have a history of adverse reactions to this antibiotic. In such situations, alternative antibiotics may be prescribed, such as doxycycline or tetracycline. These antibiotics are typically taken orally and are effective in treating latent syphilis.
It is crucial to complete the full course of antibiotic treatment as prescribed by a healthcare professional, even if symptoms have resolved or if there are no visible signs of syphilis. This is because the bacteria can still be present in the body and may cause complications if left untreated. Regular follow-up appointments and testing may be recommended to monitor the effectiveness of the treatment and ensure that the infection has been successfully cleared.
| Pros of antibiotic treatment for latent syphilis: | Cons of antibiotic treatment for latent syphilis: |
|---|---|
|
|
treatment options for latent syphilis primarily involve the use of antibiotics, such as penicillin, doxycycline, or tetracycline. These medications are effective in clearing the infection and preventing further complications. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan based on individual circumstances. Completing the full course of treatment and attending follow-up appointments are essential for successful management of latent syphilis.
Managing Tertiary Syphilis With Antibiotics
Tertiary syphilis is the most advanced stage of syphilis infection, which occurs when the initial infection is left untreated or inadequately treated. At this stage, the bacteria have spread throughout the body, leading to severe complications. Managing tertiary syphilis requires a multidisciplinary approach, often involving the use of antibiotics to control the infection and prevent further damage.
In the case of tertiary syphilis, antibiotics play a crucial role in eradicating the causative bacteria, known as Treponema pallidum. The choice of antibiotics depends on various factors, including the patient’s medical history, allergies, and the severity of the disease. One commonly used antibiotic for managing tertiary syphilis is benzathine penicillin G, administered as a single intramuscular injection.
In addition to benzathine penicillin G, other antibiotics can also be used as alternatives. These include doxycycline and tetracycline, which are effective in treating early stages of syphilis. However, their usage may be limited in certain cases due to contraindications or adverse reactions. Therefore, it is crucial for healthcare providers to carefully evaluate the patient’s individual circumstances before prescribing any particular antibiotic.
Combination Therapy For Neurosyphilis
Neurosyphilis is a form of syphilis that affects the central nervous system, including the brain and spinal cord. It is a serious condition that requires prompt and effective treatment. One of the recommended treatment approaches for neurosyphilis is combination therapy. This involves the use of two or more antibiotics to target the underlying infection and prevent further progression of the disease.
Combination therapy for neurosyphilis is crucial due to several reasons. Firstly, the bacteria that causes syphilis, known as Treponema pallidum, has the ability to develop resistance to antibiotics. By using a combination of antibiotics, the likelihood of the bacteria developing resistance is significantly reduced. This ensures that the treatment remains effective in eliminating the infection.
Furthermore, neurosyphilis is a complex condition that requires thorough treatment. The bacteria can penetrate the blood-brain barrier, making it challenging for antibiotics to reach the affected areas. By using a combination of antibiotics with different mechanisms of action, the treatment can effectively target the bacteria in different ways, increasing the chances of successful eradication.
Combination therapy also helps to minimize the risk of treatment failure and relapse. Syphilis is known for its ability to reemerge even after successful treatment. By using multiple antibiotics, the treatment can cover a wider range of the bacterial population, reducing the chances of any resistant strains surviving. This reduces the risk of relapse and ensures long-term recovery.
- Combination therapy for neurosyphilis typically involves the use of intravenous (IV) antibiotics. The most commonly used antibiotics include penicillin, ceftriaxone, and doxycycline. These medications are administered over a period of several weeks, depending on the severity of the infection. The exact combination and duration of treatment may vary based on the individual patient’s condition and response to therapy.
- It is important to note that the use of combination therapy for neurosyphilis should always be guided by a healthcare professional. They will consider various factors such as the stage and severity of the infection, the patient’s medical history, and any potential drug interactions. Close monitoring is essential to ensure the effectiveness of the treatment and to manage any potential side effects that may arise.
| Potential Benefits of Combination Therapy for Neurosyphilis |
|---|
| Enhanced treatment efficacy |
| Reduced risk of antibiotic resistance |
| Improved penetration of antibiotics into the central nervous system |
| Minimized risk of treatment failure and relapse |
| Increased chances of complete eradication of the infection |
combination therapy is a valuable approach for the treatment of neurosyphilis. By utilizing multiple antibiotics, this treatment strategy ensures better eradication of the infection, reduces the risk of antibiotic resistance, and increases the chances of long-term recovery. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for appropriate guidance and monitoring throughout the treatment process. Neurosyphilis should be taken seriously, and prompt and effective treatment can help prevent further complications and improve the overall outcome for patients.
Potential Side Effects Of Syphilis Medications
When it comes to the treatment of syphilis, medications play a crucial role in combating the infection. However, like any other medication, there are potential side effects that individuals need to be aware of. These side effects can range from mild and manageable to severe and require immediate medical attention. It is important for patients and healthcare providers to be familiar with these potential side effects to ensure the safe and effective use of syphilis medications.
One of the most common side effects of syphilis medications is gastrointestinal disturbances. This can include symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal pain. These side effects are usually temporary and resolve on their own after a few days or weeks of starting the medication. It is important for patients to stay well-hydrated and follow any dietary recommendations provided by their healthcare provider to help alleviate these symptoms.
Another potential side effect of syphilis medications is allergic reactions. Some individuals may develop an allergic reaction to the medication, which can manifest as skin rashes, itching, hives, or swelling of the face, lips, or tongue. If any of these symptoms occur, it is important to seek immediate medical attention, as allergic reactions can be life-threatening. Healthcare providers should be informed about any known allergies or sensitivities to medications to avoid prescribing medications that may trigger an allergic reaction.
- In rare cases, syphilis medications can cause more serious side effects such as liver damage or blood disorders. Liver damage may manifest as yellowing of the skin or eyes, dark urine, pale stools, or abdominal pain. Blood disorders can result in symptoms such as unusual bleeding or bruising, fatigue, or shortness of breath. These side effects require immediate medical attention and should be reported to the healthcare provider promptly. Regular monitoring of liver function and blood counts is typically recommended during the course of syphilis treatment to detect and manage these potential side effects.
| Side Effect | Description |
|---|---|
| Gastrointestinal disturbances | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain |
| Allergic reactions | Skin rashes, itching, hives, swelling of face, lips, or tongue |
| Liver damage | Yellowing of skin or eyes, dark urine, pale stools, abdominal pain |
| Blood disorders | Unusual bleeding or bruising, fatigue, shortness of breath |
while syphilis medications are essential in treating the infection, they can also have potential side effects. It is important for patients to be aware of these side effects and communicate with their healthcare providers if they experience any concerning symptoms. Regular monitoring and follow-up visits are crucial to ensure the safe and effective management of syphilis treatment. By being vigilant and proactive, individuals can minimize the impact of these potential side effects and achieve successful outcomes in their syphilis treatment journey.
Tips For Proper Medication Adherence
Proper medication adherence is crucial for individuals who are undergoing treatment for various medical conditions, including syphilis. Adherence refers to the extent to which a person follows the prescribed treatment plan, which includes taking medication as directed by their healthcare provider. It is essential for patients to adhere to their medication regimen to ensure the effectiveness of the treatment and prevent complications.
One of the key tips for proper medication adherence is to understand the importance of the prescribed treatment. Patients should have a clear understanding of why they are taking the medication, how it will benefit their health, and the potential consequences of non-adherence. This knowledge can serve as a motivating factor for individuals to adhere to their medication regimen.
Another important aspect of adherence is establishing a routine. Taking medication at the same time each day can help individuals incorporate it into their daily lives. Setting reminders, using pill organizers, or incorporating medication-taking into existing daily routines, such as brushing teeth or eating meals, can be helpful strategies to ensure consistency in adherence.
- Furthermore, effective communication with healthcare providers is vital for proper medication adherence. Patients should openly discuss any concerns, difficulties, or side effects they may experience with their healthcare provider. This enables healthcare providers to address any potential issues and provide appropriate solutions or adjustments to the treatment plan.
- patients should be proactive in educating themselves about their medication. This includes understanding the proper dosage, potential side effects, and any specific instructions for storage or administration. A well-informed patient is more likely to adhere to the prescribed treatment plan.
| Benefits of Proper Medication Adherence: |
|---|
| 1. Improved Treatment Outcomes: Adhering to the medication regimen as prescribed can lead to better treatment outcomes. This is especially important for conditions like syphilis, where proper treatment adherence can help eradicate the infection and prevent further complications. |
| 2. Prevention of Drug Resistance: Non-adherence to medication regimens can contribute to the development of drug resistance. By following the prescribed treatment plan, patients minimize the risk of developing drug-resistant strains of syphilis or other infections. |
| 3. Minimization of Complications: Proper adherence to medication can help prevent or minimize the occurrence of complications associated with syphilis and other medical conditions. By effectively managing and treating the infection, patients can reduce the likelihood of long-term damage to organs or other bodily systems. |
Drug Interactions And Precautions
When it comes to treating syphilis, the use of medications is an essential part of the process. However, it is crucial to be aware of potential drug interactions and take necessary precautions to ensure the effectiveness and safety of the treatment. Drug interactions occur when one medication affects the way another medication works, either by increasing or decreasing its effectiveness or causing unwanted side effects. Precautions, on the other hand, involve taking necessary measures to minimize the risks associated with drug interactions and ensure the successful management of syphilis.
One important aspect of avoiding drug interactions is to provide your healthcare provider with a detailed list of all the medications you are currently taking. This includes prescription drugs, over-the-counter medications, as well as any herbal supplements or vitamins. It is crucial to disclose this information to your healthcare provider, as they can evaluate potential interactions and make informed decisions regarding your treatment plan. Even seemingly harmless medications or supplements can sometimes interact with syphilis medications, so it is best to err on the side of caution and disclose everything.
In addition to disclosing your medication history, it is also necessary to follow the prescribed dosage and instructions carefully. Deviating from the recommended dose or schedule can increase the risk of drug interactions. Taking medication beyond the prescribed duration or stopping it prematurely can also hinder the effectiveness of the treatment and potentially contribute to the development of drug-resistant strains of syphilis. It is crucial to strictly adhere to the prescribed regimen and consult with your healthcare provider before making any changes to the treatment plan.
- Table: Common Medications Used in Syphilis Treatment
| Medication | Class | Possible Side Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Penicillin | Antibiotic | Allergic reactions, nausea, diarrhea |
| Doxycycline | Antibiotic | Skin sensitivity to sunlight, upset stomach |
| Tetracycline | Antibiotic | Discolored teeth, nausea, diarrhea |
| Azithromycin | Antibiotic | Nausea, diarrhea, abdominal pain |
| Ceftriaxone | Antibiotic | Injection site reactions, nausea, diarrhea |
It’s important to remember that not all medications are suitable for everyone. Certain individuals may have specific contraindications or conditions that require extra precautions when it comes to drug interactions. For example, pregnant women, individuals with liver or kidney problems, or those with a history of allergic reactions to certain medications may require adjustments in their treatment plan. Your healthcare provider will consider these factors and choose the most appropriate medications to minimize the risk of drug interactions and ensure the effectiveness of the treatment.
understanding and managing drug interactions and taking necessary precautions are crucial aspects of syphilis treatment. By disclosing your medication history, following the prescribed dosage and instructions, and discussing any concerns or potential contraindications with your healthcare provider, you can ensure that your treatment is safe and successful. Remember, effective communication and adherence to the treatment plan are key to managing syphilis and preventing complications.
The Future Of Syphilis Treatment: Research And Development
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum. Over the years, this disease has evolved and become a global health concern. While diagnosis and treatment have improved significantly, the future of syphilis treatment lies in ongoing research and development. Scientists and medical professionals are continuously exploring new strategies and therapies to combat this infectious disease and its complications.
One area of research focuses on developing more effective diagnostic tools for syphilis. Currently, the standard method of diagnosis involves serological tests to detect antibodies produced by the immune system in response to the infection. However, these tests may not always provide accurate results, particularly during the early stages of the disease. Researchers are investigating alternative diagnostic approaches, such as nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs), that can directly detect the presence of the bacterium itself, thus improving the accuracy and speed of diagnosis.
Treatment options for syphilis have primarily relied on antibiotics, especially the use of penicillin. While penicillin remains highly effective, the emergence of drug-resistant strains of Treponema pallidum presents a challenge. As a result, researchers are working on developing alternative antibiotics or combination therapies to combat drug resistance and improve treatment outcomes. Understanding the mechanisms of drug resistance is crucial in guiding the development of new medications.
- Research is also focusing on prevention strategies to curb the spread of syphilis. These strategies include developing vaccines to provide long-lasting immunity against the infection. Vaccines can stimulate the immune system to recognize and target Treponema pallidum specifically, preventing the infection from taking hold. While a commercially available vaccine for syphilis is not yet a reality, ongoing research in this area holds promise for the future.
| Challenge | Research focus |
|---|---|
| Drug resistance | Developing alternative antibiotics and combination therapies |
| Inaccurate diagnosis | Exploring new diagnostic tools, such as NAATs |
| Prevention | Developing vaccines against Treponema pallidum |
The future of syphilis treatment lies in the continuous collaboration between researchers, healthcare providers, and organizations dedicated to combating this infectious disease. By investing in research and development, we can hope to achieve better diagnostic accuracy, novel treatment options, and effective prevention strategies. As advancements continue, the future holds promise for improved outcomes and a reduced burden of syphilis worldwide.