Primary Stage: Initial Symptoms And Signs
The primary stage of a particular medical condition refers to the initial symptoms and signs that occur after the person is exposed to the disease-causing agent. This stage is crucial in identifying and diagnosing the condition early on, allowing for timely treatment and management. Recognizing the primary stage symptoms and signs is essential to prevent progression to more severe stages of the illness. In this blog post, we will explore the common initial symptoms and signs that individuals may experience during the primary stage of this condition.
During the primary stage, individuals may experience a range of symptoms that vary depending on the specific disease. Some common initial symptoms include fever, fatigue, and painless sores on or around the site of infection. These sores are often small and may go unnoticed, leading to delayed diagnosis and treatment. It is important to monitor any unusual or persistent sores, especially if they do not heal within a reasonable timeframe.
Another significant symptom during the primary stage is swollen lymph nodes. Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped structures that play a vital role in the body’s immune response. When an infection occurs, the lymph nodes near the affected area may become enlarged and tender to the touch. Swollen lymph nodes can be an early indication that the body is reacting to an infection, and medical attention should be sought if this symptom occurs.
| Common Initial Symptoms and Signs: |
|---|
| Fever |
| Fatigue |
| Painless sores |
| Swollen lymph nodes |
- Primary stage:
- Initial symptoms and signs
Early flu-like symptoms, such as fever and fatigue, are also commonly experienced during the primary stage. These symptoms can often be mistaken for a regular flu or common cold. However, it is important to be aware of any persistent or recurring symptoms and seek medical advice if necessary. Prompt diagnosis and treatment during the primary stage can help prevent the disease from progressing to more severe stages and potentially causing long-term complications.
the primary stage of a particular medical condition is characterized by the initial symptoms and signs that occur after exposure to the disease-causing agent. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis and effective treatment. Some common initial symptoms include fever, fatigue, painless sores, and swollen lymph nodes. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper assessment and appropriate management.
Secondary Stage: Widespread Rash And Flu-Like Symptoms
The secondary stage of a certain condition is characterized by widespread rash and flu-like symptoms. It is an important stage to be aware of, as it signifies the progression of the condition if left untreated. During this stage, the rash typically appears all over the body, including the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet. The rash may be accompanied by flu-like symptoms such as fever, fatigue, headache, and muscle aches.
The rash in the secondary stage is usually not itchy, but it can be coarser and more prominent than the rash in the primary stage. It may appear as red, brown, or pink rash that is flat or slightly raised. The rash can take various forms, including spots, patches, or lesions. These rash manifestations are often non-specific and can resemble other common skin conditions, making diagnosis difficult without further medical evaluation.
In addition to the rash, individuals in the secondary stage may experience flu-like symptoms. These symptoms can include a high fever, chills, sore throat, swollen lymph nodes, and body aches. The flu-like symptoms can persist for several weeks, leading to a general feeling of fatigue and malaise. It is important to note that the severity and duration of these symptoms can vary from person to person.
- Secondary Stage: Widespread Rash And Flu-Like Symptoms
| Primary Symptoms | Secondary Symptoms | Latent Symptoms | Late Symptoms |
| Fever and fatigue | Widespread rash and flu-like symptoms | No apparent symptoms | Long-term complications |
Latent Stage: No Apparent Symptoms
The latent stage of a certain medical condition is a period where there are no apparent symptoms present. This stage occurs after the initial and secondary stages, and before the late stage. During the latent stage, individuals may not be aware that they have the condition and may not seek medical attention. It is important to understand the characteristics of the latent stage in order to prevent the progression of the condition and minimize the risk of long-term complications.
One key feature of the latent stage is the absence of any noticeable symptoms. Individuals may not experience any physical discomfort or outward signs of the condition during this period. This can make it difficult to detect the presence of the condition and may delay diagnosis and treatment.
Despite the lack of apparent symptoms, the condition may still be present in the body. The pathogens or underlying factors causing the condition may continue to affect the body’s systems. This stage can vary in duration, with some conditions having a shorter latent period while others may have a longer one.
- In some cases, individuals may continue with their daily activities without realizing that they are at risk or already affected by the condition. This lack of awareness can be problematic as it may lead to the unintentional spread of the condition to others. It is important to educate individuals about the latent stage and promote regular screenings to detect the condition early.
| Key Points: |
|---|
| The latent stage is characterized by the absence of apparent symptoms. |
| Individuals may continue their daily activities without realizing they are affected. |
| Regular screenings are important to detect the condition early and prevent its spread. |
Late Stage: Long-Term Complications
In the late stage of a certain disease, long-term complications can arise that can significantly impact a person’s health and quality of life. This stage typically occurs when the disease has been left untreated or improperly managed for an extended period of time. It is important to understand the potential complications associated with the late stage of this disease, as early detection and treatment can help prevent or minimize these adverse effects.
One of the most concerning long-term complications of the late stage is the damage it can cause to various organs in the body. As the disease progresses, it can lead to damage to organs such as the heart, brain, liver, and kidneys. This can result in a range of symptoms and complications, including heart failure, cognitive impairments, liver dysfunction, and kidney failure. These complications can be debilitating and significantly impact a person’s overall health and well-being.
Another potential long-term complication of the late stage is the development of chronic pain. The disease can cause inflammation and damage to the nerves, leading to persistent pain in various parts of the body. This can greatly affect a person’s mobility, daily activities, and overall quality of life. Managing chronic pain in the late stage can be challenging, requiring a multidisciplinary approach that may include pain medications, physical therapy, and other interventions.
- Furthermore, the late stage of the disease can also weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to other infections and diseases. With a compromised immune system, the body’s ability to fight off infections and heal damaged tissues is reduced. This can result in recurrent infections, slow wound healing, and an increased risk of developing other chronic illnesses.
| Complication | Description |
|---|---|
| Organ damage | Damage to organs such as the heart, brain, liver, and kidneys, leading to various symptoms and complications. |
| Chronic pain | Inflammation and nerve damage causing persistent pain throughout the body, significantly impacting daily life. |
| Weakened immune system | Reduced ability to fight off infections and heal damaged tissues, increasing susceptibility to other illnesses. |
Painless Sores: A Common Early Sign
When it comes to recognizing the early signs of certain medical conditions, it is essential to have a comprehensive understanding of the symptoms. In the case of certain diseases, such as sexually transmitted infections (STIs), one of the common early signs to look out for is the presence of painless sores. These sores, also known as ulcers or lesions, may appear on different parts of the body, depending on the specific infection. Although painless, these sores should never be dismissed lightly, as they can signal the presence of a serious underlying health issue.
Diagnosing the exact cause of painless sores may require medical consultation and proper testing. For instance, in the case of genital herpes, painless sores often appear on or around the genitals, rectum, or mouth. These sores are typically small, fluid-filled blisters that can be easily overlooked as they are painless and may not cause immediate discomfort. However, it is important to note that while the sores may not be painful, they are highly contagious, especially when they are open or in the blister stage.
In addition to genital herpes, other STIs, such as syphilis and chancroid, can also present with painless sores. Syphilis, in particular, is characterized by the appearance of a small, painless sore known as a chancre. The chancre usually arises at the site of initial infection, such as the genitals, anus, or mouth. Chancroid, on the other hand, leads to the development of one or more painful sores, which can break open and form ulcers. However, it’s important to specifically distinguish between painless and painful sores, as the latter may be due to different causes, such as trauma or other skin conditions.
- Genital herpes: Painless sores on or around the genitals, rectum, or mouth.
- Syphilis: Painless sores known as chancres, appearing at the site of infection (genitals, anus, or mouth).
- Chancroid: Painful sores that can break open and form ulcers.
| STI | Common Early Signs |
|---|---|
| Genital herpes | Painless sores on or around the genitals, rectum, or mouth. |
| Syphilis | Painless sores known as chancres, appearing at the site of infection (genitals, anus, or mouth). |
| Chancroid | Painful sores that can break open and form ulcers. |
Fever And Fatigue: Early Flu-Like Symptoms
When it comes to identifying and understanding the early symptoms of various illnesses, fever and fatigue are often the first indicators that something may be wrong. In the case of certain infections, such as the flu, these symptoms can be particularly concerning. Fever, characterized by an elevated body temperature, and fatigue, a state of extreme tiredness and lack of energy, are key signs that the body is mounting a defense against a foreign invader.
Experiencing a fever is the body’s way of fighting off infections. The rise in body temperature is a response triggered by the immune system as it releases chemicals to help combat the invading pathogens. By increasing body heat, the immune system endeavors to create an environment that is less ideal for the pathogen’s survival and replication. Fever is a common manifestation of the flu, as well as many other viral and bacterial infections.
Alongside fever, fatigue is another early symptom that can often be perceived when the body is fighting off infection. Fatigue is an overall feeling of tiredness and lack of energy that can significantly impact a person’s ability to function and perform daily tasks. It is the body’s way of conserving energy and directing resources towards the immune system’s efforts to combat the infection. While fatigue is a non-specific symptom and can arise from various causes, its presence in conjunction with fever can help differentiate flu-like symptoms from those of other illnesses.
- Both fever and fatigue serve as warning signs that the body is encountering an infection.
- Fever helps create an unfavorable environment for pathogens, hindering their survival and multiplication.
- Fatigue is your body’s attempt to prioritize its limited energy resources towards fighting off the infection.
| Advantages of recognizing early flu-like symptoms: | Disadvantages of ignoring early flu-like symptoms: |
|---|---|
|
|
Swollen Lymph Nodes: Body’s Reaction To Infection
Swollen lymph nodes are a common symptom that occurs when the body is fighting off an infection. Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped glands located throughout the body, including the neck, armpits, and groin. They play a crucial role in the immune system by filtering lymph fluid and trapping viruses, bacteria, and other harmful substances. When an infection occurs, the lymph nodes near the affected area may become swollen, tender, and painful. This is often a sign that the body is mounting an immune response to eliminate the infection.
Swollen lymph nodes can occur due to various types of infections, including viral, bacterial, and fungal infections. Common examples include the flu, strep throat, and mononucleosis. In some cases, the swelling may be localized to one area, such as an infected cut or scratch. In other instances, multiple lymph nodes throughout the body may become swollen. The severity of the swelling can vary, ranging from barely noticeable to significantly enlarged and tender to the touch.
- It is important to note that swollen lymph nodes alone are not always indicative of a serious underlying condition. In many cases, they are simply a sign that the body’s immune system is working properly to fight off an infection. However, there are situations where swollen lymph nodes may warrant medical attention. If the swelling is accompanied by other concerning symptoms such as persistent fever, unexplained weight loss, or night sweats, it is recommended to seek medical advice. if the swelling persists for more than two weeks or continues to worsen, a healthcare professional should be consulted.
| Possible causes of swollen lymph nodes: | |
|---|---|
| Infections: | Bacterial, viral, and fungal infections can cause lymph nodes to swell. |
| Immune disorders: | Conditions such as lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, and HIV/AIDS can lead to swollen lymph nodes. |
| Cancers: | Lymphoma, leukemia, and other cancers can cause lymph nodes to become enlarged. |
| Medications: | Certain medications, such as those used for seizures or allergies, can trigger lymph node swelling as a side effect. |
When evaluating swollen lymph nodes, a healthcare provider will typically consider the patient’s medical history, perform a physical examination, and may order additional tests, such as blood tests or imaging studies, to determine the underlying cause. The treatment of swollen lymph nodes depends on the underlying condition. For example, if the swelling is due to a bacterial infection, antibiotics may be prescribed. If a viral infection is the cause, rest and over-the-counter pain relievers may be recommended to alleviate symptoms.
swollen lymph nodes are the body’s natural response to infection. While they can be concerning, especially when accompanied by other symptoms, it is important to remember that they often indicate a healthy immune system at work. However, if you have persistent or worsening swelling, or if other worrisome symptoms are present, it is advisable to seek medical attention for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
Skin Rash: Widespread, Non-Itchy Rash
A skin rash is a common symptom that can occur in various medical conditions. In this blog post, we will focus on a specific type of skin rash that is widespread and non-itchy. This type of rash can be a result of several factors, including infections, allergies, autoimmune disorders, or exposure to certain substances. It is essential to understand the characteristics and possible causes of this rash to determine the appropriate treatment and management strategies.
In dermatology, a rash is defined as a noticeable change in the texture or color of the skin. The widespread nature of this type of rash means that it can affect large areas of the body, such as the trunk, limbs, or even the face. Unlike some other rashes, this particular rash is typically non-itchy, which means that it does not cause a significant urge to scratch.
There are various possible causes for a widespread, non-itchy rash. One common cause is an allergic reaction to certain substances, such as medications, cosmetics, or certain foods. viral or bacterial infections can also lead to the development of this type of rash. Autoimmune disorders, such as lupus or psoriasis, may also present with a widespread, non-itchy rash as a symptom.
- Table: Possible Causes of Widespread, Non-Itchy Rash
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Allergic Reaction | Reaction to medications, cosmetics, or certain foods |
| Infections | Viral or bacterial infections |
| Autoimmune Disorders | Lupus, psoriasis, or other autoimmune conditions |
It is important to seek medical advice if you develop a widespread, non-itchy rash. A healthcare professional, such as a dermatologist, can evaluate your symptoms, conduct necessary tests, and determine the underlying cause of the rash. Treatment options will depend on the cause and may involve medications, lifestyle changes, or specific interventions to address the underlying condition.
a widespread, non-itchy rash can be a symptom of various medical conditions. Understanding the characteristics and possible causes of this type of rash is crucial for appropriate diagnosis and management. If you experience such a rash, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional to receive an accurate diagnosis and develop an effective treatment plan.
Patchy Hair Loss: Hair Thinning Or Bald Spots
When it comes to hair loss, there are various factors that can contribute to this common condition. One particular form of hair loss is characterized by patchy hair loss, which can manifest as thinning hair or bald spots. This condition can be distressing for individuals, as it affects their physical appearance and may impact their self-confidence. In this blog post, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and possible treatment options for patchy hair loss.
There are several potential causes of patchy hair loss. One of the most common causes is a condition known as alopecia areata. This is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the hair follicles, leading to hair loss. It often starts with small, round bald patches on the scalp, but it can also affect other hair-bearing areas of the body.
While the exact cause of alopecia areata is unknown, it is believed to be a result of a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Stress, certain medical conditions, and a family history of autoimmune disorders may increase the risk of developing this condition. It can affect individuals of all ages, including both men and women.
- Diagnosis of patchy hair loss involves a comprehensive evaluation of the individual’s medical history and a physical examination by a healthcare professional. In some cases, additional tests such as a scalp biopsy or blood tests may be necessary to rule out other underlying conditions contributing to hair loss.
-
Treatment options for patchy hair loss vary depending on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. In some cases, the hair may regrow naturally without any specific treatment. However, certain interventions can help stimulate hair growth and manage the symptoms. One common treatment option is the use of topical corticosteroids, which can help reduce inflammation in the hair follicles and promote hair regrowth. Another approach is the use of minoxidil, a medication applied directly to the scalp, which can help to stimulate hair growth. In more severe cases, systemic corticosteroids or immunomodulatory medications may be prescribed by a healthcare professional.
Muscle And Joint Pain: General Discomfort
When it comes to Lyme disease, there are various stages that individuals may experience. One of these stages is the muscle and joint pain stage, which can cause general discomfort and affect daily activities. This stage typically occurs after the initial symptoms and can last for an extended period of time if left untreated. It is essential to understand the symptoms and seek proper medical attention to manage this stage effectively.
The muscle and joint pain stage is characterized by persistent discomfort in the muscles and joints. This pain may vary in intensity and can be accompanied by stiffness and swelling. Individuals may find it challenging to perform regular tasks, such as walking or lifting objects, due to the discomfort. In some cases, the pain may migrate from one area to another, making it difficult to pinpoint the exact source of the discomfort.
In addition to muscle and joint pain, individuals may also experience fatigue and weakness. These symptoms can further contribute to the overall discomfort and limit one’s ability to engage in physical activities. It is crucial to rest and allow the body to recover during this stage, as overexertion can worsen the symptoms.
- During the muscle and joint pain stage, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. The physician may order blood tests or perform a physical examination to assess the extent of the symptoms. Treatment options may include antibiotics to target the underlying infection and anti-inflammatory medications to alleviate the pain and swelling.
| Key Points: |
|---|
| 1. The muscle and joint pain stage is a common symptom of Lyme disease. |
| 2. The discomfort can affect everyday activities and may be accompanied by fatigue. |
| 3. Seeking medical attention is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. |
| 4. Treatment options may include antibiotics and anti-inflammatory medications. |
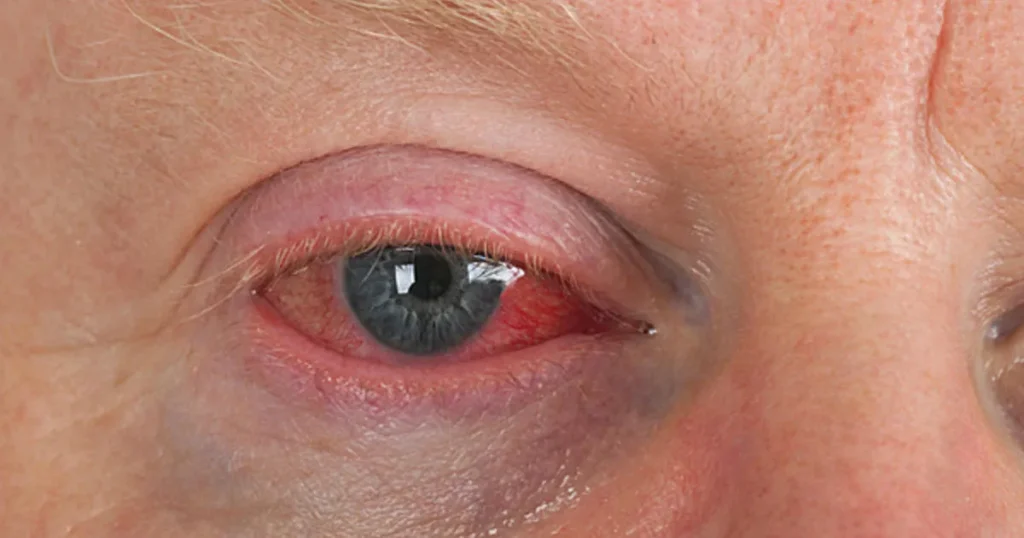
Vision Problems: Blurred Or Loss Of Vision
One common symptom experienced by individuals with certain medical conditions is vision problems, which can manifest as either blurred vision or loss of vision. Vision problems can be distressing and have a significant impact on daily life, making it difficult to perform tasks that require visual acuity. In this blog post, we will explore the causes of vision problems, the potential underlying conditions that may contribute to them, and the available treatment options.
Causes of Vision Problems:
There are various factors that can result in blurred vision or loss of vision. One common cause is refractive errors, which occur when the shape of the eye prevents light from focusing directly on the retina. This can lead to nearsightedness, farsightedness, or astigmatism, all of which can affect visual clarity. Other causes include eye infections or injuries, cataracts, glaucoma, and macular degeneration.
Underlying Conditions:
Vision problems can also be a symptom of underlying medical conditions. For instance, individuals with diabetes may experience diabetic retinopathy, a condition that damages the blood vessels in the retina. certain autoimmune disorders such as multiple sclerosis, lupus, or rheumatoid arthritis can cause inflammation of the optic nerve or the retina, leading to vision issues. It is crucial to consult a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause of vision problems and receive appropriate treatment.
Treatment Options:
The treatment for vision problems depends on the underlying cause. Refractive errors are often corrected with eyeglasses, contact lenses, or refractive surgeries such as LASIK. In cases where the vision problems are due to underlying medical conditions, treating the root cause becomes paramount. This may involve managing the underlying illness, using medications to control inflammation or blood sugar levels, or even surgical interventions. Regardless of the cause, early detection and intervention can significantly improve the prognosis and prevent further deterioration of vision.
- Summary
Vision problems can manifest as blurred or loss of vision, and they are often caused by refractive errors, eye infections or injuries, cataracts, glaucoma, or macular degeneration. However, they can also be symptoms of underlying medical conditions such as diabetic retinopathy or autoimmune disorders. Treatment options include corrective eyewear, surgical procedures, managing the underlying illness, or using medications to control inflammation or blood sugar levels. Early detection and appropriate treatment are essential for preserving and improving vision.
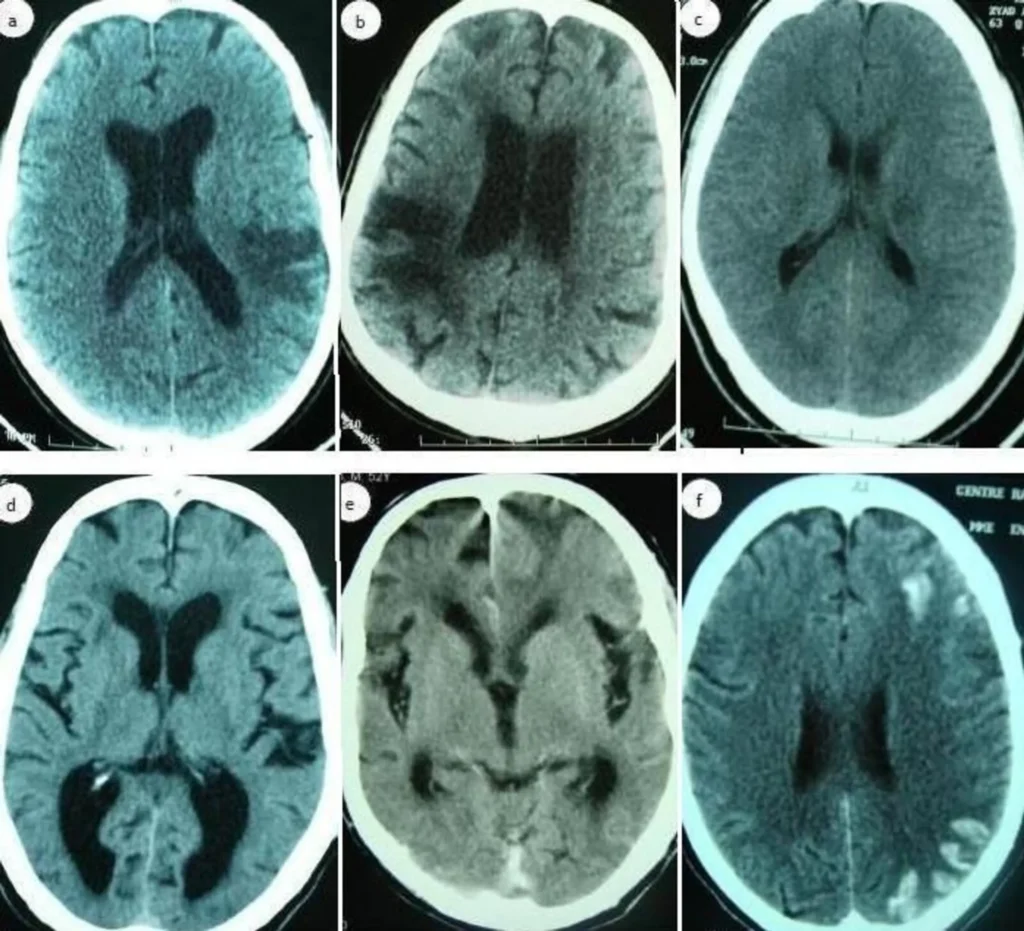
Neurological Symptoms: Memory Loss And Coordination Issues
Neurological symptoms associated with memory loss and coordination issues can be indicators of a range of underlying conditions. These symptoms can occur due to various factors, such as aging, trauma, or neurological disorders. Memory loss refers to the inability to recall information or events, while coordination issues involve difficulties in maintaining balance and performing precise movements. Both of these symptoms can significantly impact an individual’s daily functioning and quality of life.
When it comes to memory loss, it is important to distinguish between normal age-related forgetfulness and more severe forms of memory impairment. Occasional forgetfulness is a natural part of the aging process and may not necessarily indicate a serious underlying condition. However, persistent and worsening memory loss could be a sign of conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease or other forms of dementia. Seeking medical advice is crucial in order to determine the cause and appropriate management strategies.
In addition to memory loss, coordination issues can also be a cause for concern. Impaired coordination can manifest as difficulty in walking, maintaining balance, or performing precise movements such as writing or buttoning a shirt. These symptoms may arise from neurological conditions such as Parkinson’s disease, multiple sclerosis, or cerebellar disorders. Proper evaluation and diagnosis from a healthcare professional are essential to identify the underlying cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
- It is worth noting that memory loss and coordination issues can sometimes be associated with other symptoms that further aid in the diagnosis process. For instance, individuals experiencing these neurological symptoms may also present with difficulties in concentration, speech problems, or mood changes. the presence of other neurological symptoms may help narrow down the potential causes and guide healthcare professionals in their assessment.
| Some common causes of neurological symptoms: |
|---|
| 1. Alzheimer’s disease |
| 2. Parkinson’s disease |
| 3. Multiple sclerosis |
| 4. Traumatic brain injury |
| 5. Stroke |
neurological symptoms such as memory loss and coordination issues should not be ignored or dismissed as normal signs of aging. These symptoms can be indicative of various underlying conditions, ranging from minor to more severe neurodegenerative disorders. Seeking medical attention and receiving timely diagnosis and treatment are essential for proper management and preserving one’s overall well-being.