Neurosyphilis: The Devastating Effects On The Nervous System
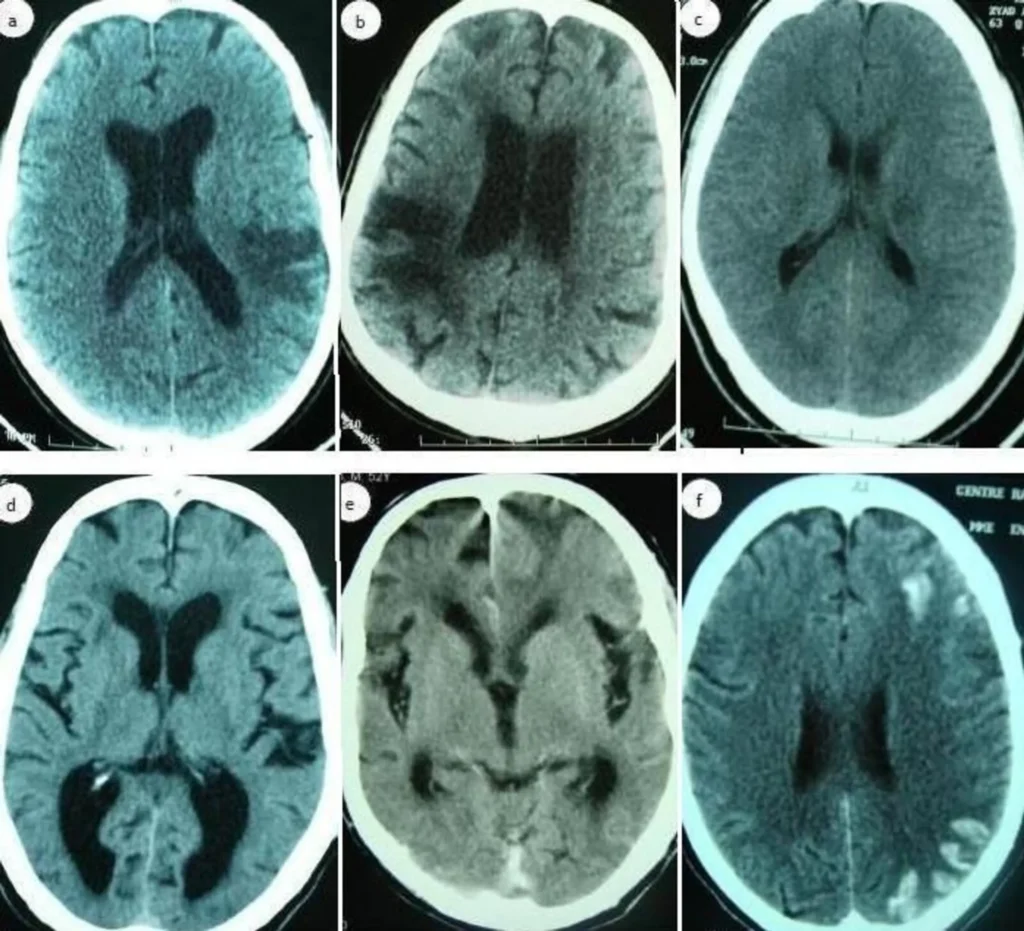
Neurosyphilis is a severe neurological complication caused by the bacteria Treponema pallidum, which is responsible for the sexually transmitted infection syphilis. This condition affects the nervous system and can have devastating effects if left untreated. It can lead to various neurological symptoms and complications, affecting both the central and peripheral nervous systems.
One of the most common manifestations of neurosyphilis is meningitis, where the protective membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord become inflamed. This inflammation can cause severe headaches, fever, and neck stiffness. neurosyphilis can lead to the development of syphilitic gummas, which are firm, tumor-like nodules that can form in various areas of the brain.
The effects of neurosyphilis on the nervous system can also include cognitive impairments, such as difficulties with memory, concentration, and judgment. This can progress to more severe conditions, such as general paresis, where individuals experience problems with speech, personality changes, and motor dysfunction.
| Neurological Complications of Neurosyphilis | Effects on the Nervous System |
|---|---|
| Meningitis | Inflammation of the protective membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord |
| Syphilitic Gummas | Tumor-like nodules that can form in various areas of the brain |
| Cognitive Impairments | Difficulties with memory, concentration, and judgment |
| General Paresis | Speech problems, personality changes, and motor dysfunction |
Neurosyphilis has devastating effects on the nervous system. By understanding the potential complications, individuals can recognize the importance of early diagnosis and treatment. It is crucial to seek medical attention if any symptoms or concerns arise, as neurosyphilis can have severe consequences if left untreated. Protecting oneself from syphilis through safe sexual practices and regular testing is essential for maintaining optimal health and preventing the spread of this infection.
Cardiovascular Syphilis: How It Affects The Heart And Blood Vessels
Cardiovascular syphilis, also known as syphilitic heart disease, is a serious condition that affects the heart and blood vessels. It is caused by the bacteria Treponema pallidum, which is responsible for syphilis. This condition occurs in the late stages of syphilis, when the infection has been left untreated for a long time. Cardiovascular syphilis can have devastating effects on the cardiovascular system, leading to various complications and potentially life-threatening consequences.
One of the most common complications of cardiovascular syphilis is aortic aneurysm. An aneurysm is a bulging and weakening of the walls of the aorta, the main artery that carries blood from the heart to the rest of the body. In cardiovascular syphilis, the bacteria can directly invade the walls of the aorta, causing inflammation and damage. Over time, this can result in the formation of an aneurysm, which can rupture and lead to severe internal bleeding. This is a medical emergency and requires immediate treatment.
Another way cardiovascular syphilis affects the heart and blood vessels is by causing a condition known as aortic regurgitation. Aortic regurgitation occurs when the aortic valve, which separates the heart’s left ventricle from the aorta, does not close properly. As a result, blood flows back into the left ventricle instead of flowing forward into the rest of the body. This can lead to symptoms such as fatigue, shortness of breath, and chest pain. If left untreated, aortic regurgitation can cause significant strain on the heart and may eventually lead to heart failure.
- Cardiovascular syphilis can also lead to coronary artery disease, a condition characterized by the narrowing of the blood vessels that supply the heart muscles with oxygen and nutrients. This can result in reduced blood flow to the heart, leading to chest pain or angina. In severe cases, a complete blockage of the coronary arteries can occur, causing a heart attack. cardiovascular syphilis can weaken the heart muscles, a condition known as syphilitic myocarditis, making it difficult for the heart to pump blood efficiently.
| Complications of Cardiovascular Syphilis: |
|---|
| 1. Aortic aneurysm |
| 2. Aortic regurgitation |
| 3. Coronary artery disease |
| 4. Syphilitic myocarditis |
cardiovascular syphilis poses significant risks to the heart and blood vessels. It can lead to complications such as aortic aneurysm, aortic regurgitation, coronary artery disease, and syphilitic myocarditis. Early detection and treatment of syphilis are crucial in preventing these devastating effects on the cardiovascular system. If you suspect you may have syphilis or are at risk of contracting it, it is important to seek medical attention promptly to prevent further complications and protect your heart and overall health.
Ocular Syphilis: Understanding The Potential Eye Complications
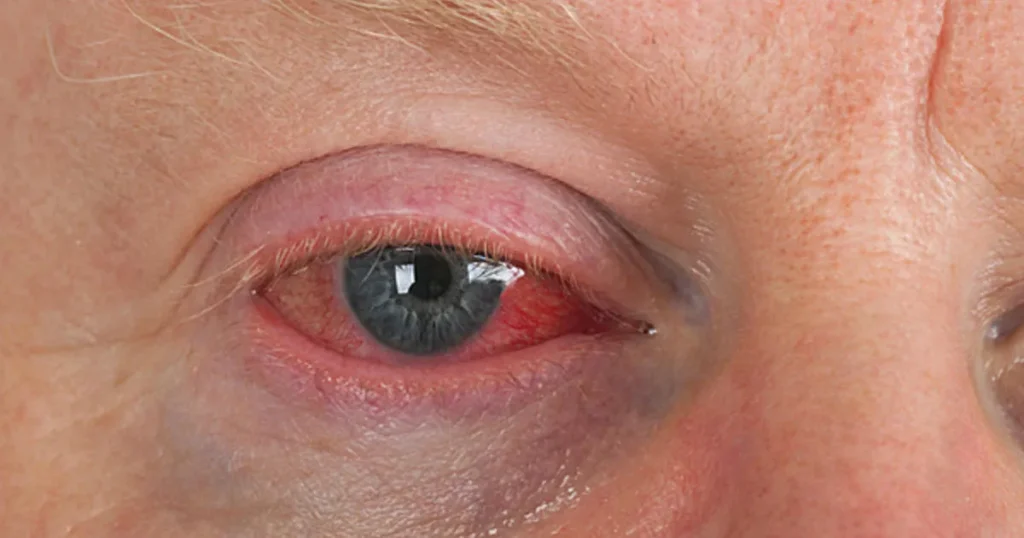
Ocular syphilis is a serious condition that occurs when syphilis bacteria infiltrates the eye. It can lead to a range of complications and may result in permanent vision loss if not treated promptly. Understanding the potential eye complications associated with ocular syphilis is crucial for early detection and effective management. In this article, we will explore the various ways syphilis can affect the eyes and discuss the importance of seeking medical attention for any concerning symptoms.
One of the most common eye complications of ocular syphilis is uveitis, which is the inflammation of the uvea – the middle layer of the eye that contains the iris, ciliary body, and choroid. Uveitis can cause eye pain, redness, light sensitivity, and blurred vision. It may affect one or both eyes and can lead to long-term damage if left untreated.
Another potential complication of ocular syphilis is retinitis, which is the inflammation of the retina – the thin layer of tissue that lines the back of the eye. Retinitis can cause vision disturbances, such as seeing floaters, flashes of light, or dark spots. If not treated promptly, retinitis can result in retinal detachment and irreversible vision loss.
Furthermore, ocular syphilis can also lead to optic neuritis, which is the inflammation of the optic nerve. The optic nerve connects the eye to the brain and is responsible for transmitting visual information. When affected by syphilis, the optic nerve may become swollen and result in vision loss, color vision abnormalities, and pain with eye movement.
- ocular syphilis can have devastating effects on the eyes and vision if left untreated. It can lead to complications such as uveitis, retinitis, and optic neuritis, all of which can result in permanent vision loss. It is essential for individuals with syphilis to be aware of the potential eye involvement and seek immediate medical attention if they experience any eye-related symptoms. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial in preventing long-term ocular complications and preserving vision. Regular screenings and safe sexual practices are also important in preventing the spread of syphilis and its ocular complications.
| Potential Eye Complications of Ocular Syphilis: |
|---|
| – Uveitis |
| – Retinitis |
| – Optic Neuritis |
Congenital Syphilis: The Risks For Infants And Long-term Consequences
Congenital syphilis is a serious condition that occurs when a pregnant woman with syphilis passes the infection to her baby during pregnancy or childbirth. This transmission can have devastating effects on the infant’s health and may result in long-term consequences if left untreated.
One of the major risks associated with congenital syphilis is low birth weight. Infected babies may be born prematurely or have stunted growth due to the impact of the infection on their developing bodies. These infants are also at a higher risk of experiencing developmental delays and learning disabilities as they grow older. It is crucial for healthcare providers to identify and treat congenital syphilis as early as possible to mitigate these risks.
Another consequence of congenital syphilis is the potential for severe organ damage. The bacteria that cause syphilis can affect various organs of the baby’s body, including the brain, liver, and bones. If left untreated, this damage can lead to serious complications such as neurologic disorders, hepatitis, and skeletal abnormalities. Regular monitoring and prompt treatment are vital in preventing long-term consequences associated with organ damage.
- Infants born with congenital syphilis are also at an increased risk of developing other infections. The weakened immune system resulting from the syphilis infection can make it easier for the baby to contract illnesses such as pneumonia or meningitis. These secondary infections can further compromise the baby’s health and require additional medical interventions.
| Long-Term Consequences | Description |
|---|---|
| Developmental Delays | Children with congenital syphilis may experience delays in reaching developmental milestones such as walking or speaking. Early intervention and appropriate therapies can help minimize the impact of these delays on the child’s overall development. |
| Hearing and Vision Problems | Syphilis can cause damage to the baby’s ears and eyes, leading to hearing loss and visual impairments. Regular vision and hearing screenings are essential to identify and address these issues early on. |
| Dental Abnormalities | The teeth of individuals who had congenital syphilis can be adversely affected, resulting in notches or deformities in the enamel. Good oral hygiene practices and regular dental check-ups can help manage these abnormalities. |
Congenital syphilis poses significant risks for infants and can have long-term consequences that affect their overall health and development. Early detection through prenatal screening and timely treatment is crucial in preventing these risks and mitigating potential complications. It is essential for healthcare providers to educate expectant mothers about syphilis, its transmission, and the importance of regular prenatal care to safeguard the well-being of both mother and child.
Gummatous Syphilis: Exploring The Tissue Destructive Complications
Gummatous syphilis is a subtype of syphilis that is characterized by the formation of gummas, which are soft, tumor-like growths that can develop in various tissues of the body. These gummas are a result of the chronic inflammation caused by untreated or inadequately treated syphilis. Although gummatous syphilis is rare in the era of antibiotic treatment, it is important to understand its potential complications and the destructive effects it can have on different tissues.
One of the key tissues affected by gummatous syphilis is the skin. Gummas can develop on the skin surface and lead to the formation of ulcers. These ulcers can be deep and non-healing, causing significant tissue damage. If left untreated, the ulcers can extend to neighboring tissues and result in disfiguring scars. It is crucial for individuals with syphilis to seek early and appropriate treatment to prevent the development of gummas and subsequent skin complications.
In addition to the skin, gummatous syphilis can affect various other tissues in the body, including the bones and joints. The chronic inflammation associated with this subtype of syphilis can lead to the destruction of bone tissue, causing lesions and deformities. Joint involvement can result in pain, swelling, and restricted movement. Without proper medical intervention, the destructive effects on the musculoskeletal system can be irreversible, leading to long-term complications.
- Gummatous syphilis can also impact the cardiovascular system. Gummas can develop in the walls of blood vessels, causing weakening and narrowing of the vessels. This can lead to serious cardiovascular complications, including aneurysms and blockages. If an aneurysm ruptures, it can be life-threatening. It is important for individuals with gummatous syphilis to undergo regular cardiovascular evaluations to detect and manage any potential complications.
- Another tissue that can be affected by gummatous syphilis is the central nervous system. The chronic inflammation can lead to the formation of gummas within the brain and spinal cord. This can result in neurological symptoms such as headaches, cognitive impairment, and even paralysis. Neurological complications require prompt treatment and close monitoring to prevent irreversible damage and disability.
| Tissue | Complications |
|---|---|
| Skin | Formation of ulcers and disfiguring scars |
| Bones and Joints | Destruction of bone tissue, lesions, and restricted movement |
| Cardiovascular System | Weakening and narrowing of blood vessels, aneurysms, and blockages |
| Central Nervous System | Formation of gummas in the brain and spinal cord, resulting in neurological symptoms |
Gummatous syphilis, although uncommon, highlights the destructive potential of untreated or poorly managed syphilis. To prevent the complications associated with gummatous syphilis, it is crucial for individuals to promptly seek medical attention upon noticing any symptoms or signs of syphilis. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are key to preventing the development of gummas and the subsequent tissue damage they can cause.
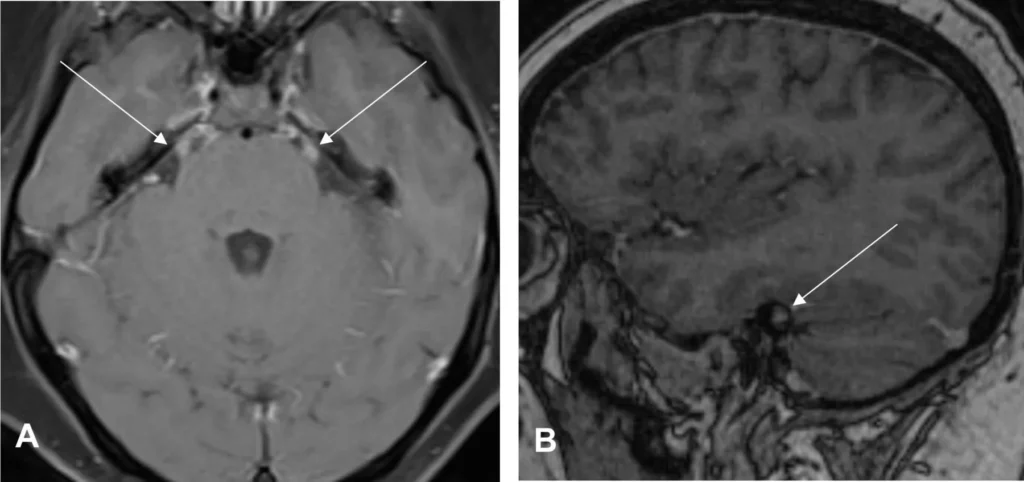
Syphilitic Meningitis: Recognizing The Inflammation Of The Brain
Syphilitic meningitis is a rare complication of syphilis that affects the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord. This condition occurs when the bacteria that causes syphilis, known as Treponema pallidum, invades the central nervous system. As a result, inflammation of the meninges, the protective layers of tissue that cover the brain and spinal cord, occurs. Syphilitic meningitis can lead to various neurological symptoms and if left untreated, it can have devastating effects on the nervous system.
One of the key symptoms of syphilitic meningitis is persistent headache. This headache is typically more severe during the night and early morning. individuals may experience neck stiffness and sensitivity to light. These symptoms are a result of the inflammation and irritation caused by the infection in the meninges. It’s important to note that the symptoms of syphilitic meningitis can vary from person to person, and some individuals may not exhibit all of the typical symptoms.
In addition to the neurological symptoms, syphilitic meningitis can also cause other complications. It can lead to cranial nerve dysfunction, which can affect vision, hearing, and facial muscles. Furthermore, individuals may experience changes in their mental state, including confusion, memory problems, and personality changes. If left untreated, syphilitic meningitis can progress to more severe complications such as seizures, paralysis, and even coma.
- Diagnosis and Treatment:
Diagnosing syphilitic meningitis involves a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. A healthcare professional will assess the individual’s symptoms, conduct a physical examination, and may order blood tests to check for the presence of Treponema pallidum antibodies. In some cases, a lumbar puncture, also known as a spinal tap, may be performed to analyze the cerebrospinal fluid for signs of infection.
Once diagnosed, syphilitic meningitis can be treated with antibiotics. The primary treatment for syphilis is penicillin, which is highly effective in eliminating the infection. Depending on the stage and severity of the disease, a course of intravenous or intramuscular antibiotic therapy may be recommended. It’s crucial to complete the full course of treatment as prescribed by the healthcare provider to ensure eradication of the infection and prevent potential complications.
| Recognizing Syphilitic Meningitis | Treatment and Prevention |
|---|---|
| Symptoms of persistent headache, neck stiffness, and light sensitivity | Diagnosis through clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and imaging |
| Neurological complications including cranial nerve dysfunction and mental state changes | Antibiotic treatment with penicillin to eradicate the infection |
| Potential progression to severe complications such as seizures and paralysis | Completing the full course of treatment to prevent complications |
Syphilitic meningitis is a serious condition that requires prompt recognition and treatment. It is important for individuals who are at risk of syphilis or experiencing symptoms to seek medical attention. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent further damage to the nervous system and improve long-term outcomes. Remember, practicing safe sex and getting regular screenings for sexually transmitted infections are crucial steps in preventing syphilis and its complications.
Syphilis And The Skin: Unveiling The Cutaneous Manifestations
Syphilis, a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum, is notorious for its wide range of manifestations throughout the body. One of the areas commonly affected by syphilis is the skin. Cutaneous manifestations of syphilis can vary in appearance and severity, and can present at different stages of the disease. Understanding these skin manifestations is crucial for early diagnosis and proper management of syphilis.
Primary syphilis, which occurs shortly after the initial infection, often presents with a solitary painless ulcer known as a chancre. This ulcer typically develops at the site of sexual contact with an infected individual. The chancre is usually round, firm, and non-tender. It can appear anywhere on the body, including the genital region, mouth, or anus. The chancre is highly infectious and can persist for several weeks before spontaneously healing.
Secondary syphilis, the stage that follows primary syphilis, is characterized by widespread rashes on the skin. These rashes can vary in appearance, ranging from pink or red macules (flat spots) to papules (raised bumps) or pustules (pus-filled bumps). The rash is typically non-itchy and can affect various parts of the body, including the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. In addition to the rash, individuals with secondary syphilis may experience other symptoms such as fever, headache, fatigue, and swollen lymph nodes.
- Tertiary syphilis, the most severe form of the disease, can lead to numerous complications, including skin manifestations. One of the characteristic cutaneous manifestations of tertiary syphilis is gumma formation. A gumma is a soft, rubbery mass that can develop in different organs, including the skin. When gummas appear on the skin, they usually present as nodules or plaques. These lesions can ulcerate or become necrotic, causing significant tissue destruction. Tertiary syphilis can also cause other skin manifestations such as syphilitic alopecia (hair loss), scleroderma-like changes, and nodular lesions called “lues”.
| Treatment and Prevention |
|---|
| Early diagnosis and prompt treatment are essential for managing syphilis and preventing complications. The primary and secondary stages of syphilis can usually be treated effectively with antibiotics such as penicillin. However, tertiary syphilis may require a more prolonged course of treatment. |
| To prevent syphilis and its cutaneous manifestations, practicing safe sex is crucial. Consistently using condoms and limiting sexual partners can significantly reduce the risk of acquiring or transmitting the infection. Regular screenings for sexually transmitted infections, including syphilis, are recommended for individuals at high risk. |
Syphilis can manifest in various ways on the skin, depending on the stage of the disease. Recognizing and understanding the different cutaneous manifestations of syphilis is crucial for early diagnosis, appropriate treatment, and prevention of complications. If you suspect you may have syphilis or have been exposed to the infection, it is important to seek medical attention promptly.
Syphilis And Joint Involvement: Examining The Musculoskeletal Complications
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum. While it primarily affects the genital area, it can also have severe consequences on other parts of the body, including the musculoskeletal system. In this blog post, we will explore the musculoskeletal complications associated with syphilis and the impact it can have on joint involvement.
One of the most common musculoskeletal complications of syphilis is known as syphilitic arthritis. This condition occurs when the bacteria infect the joints, leading to inflammation and pain. Syphilitic arthritis can affect any joint in the body, but it most commonly affects the knees, ankles, and wrists. The symptoms can vary from mild discomfort to severe joint pain and swelling. If left untreated, syphilitic arthritis can cause permanent damage to the affected joints.
In addition to syphilitic arthritis, syphilis can also lead to other musculoskeletal complications, such as tendonitis and bursitis. Tendonitis occurs when the tendons, which connect muscles to bones, become inflamed. This can cause pain, swelling, and difficulty moving the affected joint. Bursitis, on the other hand, is the inflammation of the fluid-filled sacs called bursae, which cushion the joints. It can result in pain, tenderness, and swelling around the affected joint.
| Musculoskeletal Complication | Symptoms | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Syphilitic Arthritis | Joint pain, swelling, stiffness | Antibiotics, anti-inflammatory medications |
| Tendonitis | Pain, swelling, difficulty moving joint | Rest, physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications |
| Bursitis | Pain, tenderness, swelling around joint | Rest, physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications |
If you have been diagnosed with syphilis and are experiencing any musculoskeletal symptoms, it is crucial to seek medical attention. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent further damage to the joints and improve your overall health. Your healthcare provider may prescribe antibiotics to treat the underlying syphilis infection, along with medications to manage the inflammation and pain in the affected joints.
It is important to note that syphilis and its musculoskeletal complications can be prevented through safe sexual practices, such as using condoms and getting regularly tested for sexually transmitted infections. If you suspect you may have been exposed to syphilis or are experiencing any symptoms, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Syphilis & Pregnancy: How İt Impacts Fetus And Mother’s Health
Syphilis, a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum, can have serious consequences for both the fetus and the mother during pregnancy. It is crucial for expectant mothers to understand the potential risks and complications associated with syphilis to ensure proper care and prevention.
When a pregnant woman is infected with syphilis, the bacterium can cross the placental barrier and directly impact the developing fetus. This can lead to a condition known as congenital syphilis, which can cause a range of health issues in newborns. The severity of the effects on the fetus depends on various factors such as the stage of syphilis infection in the mother and the duration of the infection.
One of the most concerning impacts of syphilis on the fetus is the risk of miscarriage or stillbirth. Syphilis can greatly increase the chances of these tragic outcomes, especially when left untreated or inadequately managed. infants born to mothers with syphilis may suffer from low birth weight, premature birth, and developmental abnormalities.
- Neurological complications: Syphilis can cause severe damage to the nervous system of the fetus. This can result in neurological disorders such as cognitive impairment, blindness, deafness, and seizures.
- Cardiovascular complications: The heart and blood vessels of the fetus can be affected by syphilis, leading to various cardiovascular abnormalities. This can include issues with heart function, valve defects, and blood vessel inflammation.
- Miscellaneous complications: Syphilis during pregnancy can also result in other complications such as bone deformities, skin rashes, and organ damage. These manifestations highlight the systemic nature of syphilis and its potential to affect multiple parts of the body.
It is important for pregnant women to undergo regular prenatal screenings for syphilis, as early detection and treatment can significantly reduce the risks to both the fetus and the mother. Treatment typically involves the administration of antibiotics, such as penicillin, under the supervision of healthcare professionals.
Syphilis can have implications for the mother’s health as well. If left untreated, it can progress to advanced stages, causing serious complications such as damage to the nervous system, heart, and other organs. It is advisable for pregnant women to prioritize their own health alongside their baby’s well-being by seeking appropriate medical care.
| Prevention Measures |
|---|
| 1. Practicing safe sex by using condoms |
| 2. Undergoing regular STI screenings before and during pregnancy |
| 3. Ensuring partners also undergo testing and treatment |
| 4. Seeking immediate medical attention if any symptoms or concerns arise |
| 5. Following healthcare providers’ guidance and recommendations for treatment |
Syphilis can have significant impacts on both the fetus and the mother during pregnancy. By understanding the potential risks and complications associated with syphilis, expectant mothers can take proactive measures to protect themselves and their unborn child. Regular screenings, early detection, and timely treatment are essential in mitigating the adverse effects of syphilis on fetal and maternal health. Remember, prevention and proactive healthcare are key.
Syphilis And Mental Health: Unraveling The Psychological Consequences
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum. While it is primarily known for its physical manifestations, such as skin rashes and ulcers, syphilis can also have profound effects on mental health. In this blog post, we will delve into the psychological consequences of syphilis and explore how the disease can impact an individual’s mental well-being.
One of the most significant psychological consequences of syphilis is neurosyphilis, which occurs when the infection spreads to the nervous system. This can lead to a range of psychiatric symptoms, including mood disturbances, personality changes, and cognitive impairments. The bacterium affects the brain and can cause inflammation, leading to conditions such as meningitis or encephalitis. These neurological complications can result in symptoms such as confusion, memory loss, and even psychosis.
In addition to neurosyphilis, syphilis can also contribute to the development or exacerbation of mental health disorders. The stigma surrounding the disease, along with the physical symptoms it presents, can negatively impact an individual’s self-esteem and body image. This, in turn, can lead to feelings of shame, embarrassment, and social isolation, which are risk factors for the development of depression, anxiety, and other mood disorders.
- Syphilis can also affect an individual’s cognitive functioning. Studies have shown that the infection can impair attention, concentration, and memory. It can also lead to difficulties with problem-solving and decision-making. These cognitive deficits can significantly impact an individual’s daily functioning and quality of life.
| The Psychological Consequences of Syphilis |
|---|
| Neurosyphilis: The infection spreading to the nervous system can cause psychiatric symptoms such as mood disturbances, personality changes, and cognitive impairments. |
| Mental Health Disorders: The stigma, physical symptoms, and social impact of the disease can contribute to the development or exacerbation of mental health disorders, including depression and anxiety. |
| Cognitive Impairment: Syphilis can impair attention, memory, problem-solving, and decision-making skills, detrimentally affecting an individual’s daily functioning. |
It is crucial for healthcare professionals to recognize the psychological consequences of syphilis and provide appropriate support and treatment. This may include accessing mental health services, such as therapy or medication, to address mood disorders and cognitive impairments. education and awareness campaigns can help reduce stigma and promote early detection and treatment of syphilis, ultimately preventing the development of mental health complications.
Syphilis not only affects the body but also has significant implications for mental health. The psychological consequences of this sexually transmitted infection can range from neurosyphilis and its associated psychiatric symptoms to the development or exacerbation of mental health disorders. Recognizing and addressing these consequences is essential to ensure the well-being and overall health of individuals affected by syphilis.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the symptoms of neurosyphilis?
The symptoms of neurosyphilis can vary, but they may include headache, difficulty concentrating, memory loss, and changes in behavior or personality.
2. How does cardiovascular syphilis affect the heart and blood vessels?
Cardiovascular syphilis can lead to aneurysms, inflammation of the heart valves, and blockages in the blood vessels, which can increase the risk of heart attack or stroke.
3. What are the potential eye complications of ocular syphilis?
Ocular syphilis can cause vision loss, inflammation of the eye tissues, and even blindness if left untreated.
4. What are the risks and long-term consequences of congenital syphilis for infants?
Infants with congenital syphilis may experience premature birth, low birth weight, developmental delays, and lifelong physical and neurological problems if not treated early.
5. How does gummatous syphilis lead to tissue destruction?
Gummatous syphilis can cause the formation of destructive masses called gummas, which can damage softer tissues like skin, bones, and internal organs.
6. What are the symptoms of syphilitic meningitis?
Syphilitic meningitis typically presents with fever, headache, neck stiffness, and sometimes seizures, and it can cause inflammation and damage to the brain and spinal cord.
7. What are the cutaneous manifestations of syphilis?
Syphilis can cause various skin manifestations, including a rash, sores, ulcers, and nodules, which can appear on any part of the body.